There is a cool computer vision library called OpenCV available. Using OpenCV, we can do stuff like object detection, feature extraction and other computer vision tasks. OpenCV is a native library, but it also comes with JNI Wrappers for Java and the Android platform.
For the beginning, i want to implement real time face detection on my Samsung Galaxy S3 with OpenCV and some Java code. Here is a screenshot of the final result:
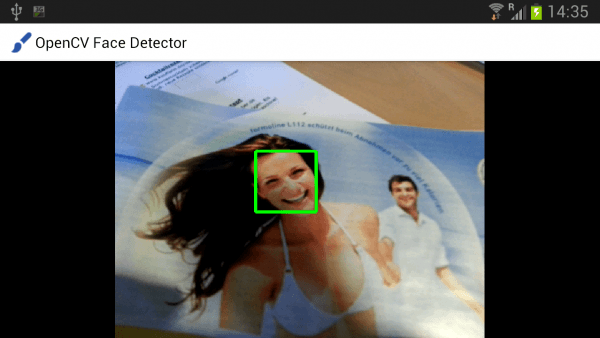
The OpenCV Android SDK comes with some handy Camera interface classes converting Android Bitmaps to OpenCV Mat instances. We can apply all computer vision tasks on such Mat instances and finally render the results. The following Android Activity shows all you need to do face detection on Android:
package de.mirkosertic.opencvtest;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import org.opencv.android.*;
import org.opencv.android.CameraBridgeViewBase.CvCameraViewListener;
import org.opencv.core.*;
import org.opencv.imgproc.Imgproc;
import org.opencv.objdetect.CascadeClassifier;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class OpenCVActivity extends Activity
implements CvCameraViewListener {
private CameraBridgeViewBase openCvCameraView;
private CascadeClassifier cascadeClassifier;
private Mat grayscaleImage;
private int absoluteFaceSize;
private BaseLoaderCallback mLoaderCallback = new BaseLoaderCallback(this) {
@Override
public void onManagerConnected(int status) {
switch (status) {
case LoaderCallbackInterface.SUCCESS:
initializeOpenCVDependencies();
break;
default:
super.onManagerConnected(status);
break;
}
}
};
private void initializeOpenCVDependencies() {
try {
// Copy the resource into a temp file so OpenCV can load it
InputStream is = getResources().openRawResource(R.raw.lbpcascade_frontalface);
File cascadeDir = getDir("cascade", Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
File mCascadeFile = new File(cascadeDir, "lbpcascade_frontalface.xml");
FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(mCascadeFile);
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
os.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
is.close();
os.close();
// Load the cascade classifier
cascadeClassifier = new CascadeClassifier(mCascadeFile.getAbsolutePath());
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("OpenCVActivity", "Error loading cascade", e);
}
// And we are ready to go
openCvCameraView.enableView();
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
getWindow().addFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON);
openCvCameraView = new JavaCameraView(this, -1);
setContentView(openCvCameraView);
openCvCameraView.setCvCameraViewListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onCameraViewStarted(int width, int height) {
grayscaleImage = new Mat(height, width, CvType.CV_8UC4);
// The faces will be a 20% of the height of the screen
absoluteFaceSize = (int) (height * 0.2);
}
@Override
public void onCameraViewStopped() {
}
@Override
public Mat onCameraFrame(Mat aInputFrame) {
// Create a grayscale image
Imgproc.cvtColor(aInputFrame, grayscaleImage, Imgproc.COLOR_RGBA2RGB);
MatOfRect faces = new MatOfRect();
// Use the classifier to detect faces
if (cascadeClassifier != null) {
cascadeClassifier.detectMultiScale(grayscaleImage, faces, 1.1, 2, 2,
new Size(absoluteFaceSize, absoluteFaceSize), new Size());
}
// If there are any faces found, draw a rectangle around it
Rect[] facesArray = faces.toArray();
for (int i = 0; i <facesArray.length; i++)
Core.rectangle(aInputFrame, facesArray[i].tl(), facesArray[i].br(), new Scalar(0, 255, 0, 255), 3);
return aInputFrame;
}
@Override
public void onResume() {
super.onResume();
OpenCVLoader.initAsync(OpenCVLoader.OPENCV_VERSION_2_4_6, this, mLoaderCallback);
}
}The OpenCV documentation is not very Android or even user friendly, it is very technical. But if you do some Google research and look at the provided Unit Test classes, you can get a feeling about the API after a few days. The code from above uses an already trained cascade provided by OpenCV to detect faces. We can create own cascades do detect all types of objects, from pencils to cars or even traffic signs. This will be my next Android app.
Stay tuned and happy coding!
